Blog | AI In Finance
The Massive Evolution From RPA to Intelligent Autonomous Applications Has Begun
 Editor's note: This article originally appeared on the blog A Software Insider's Point of View and is reposted here with permission by the author.
Editor's note: This article originally appeared on the blog A Software Insider's Point of View and is reposted here with permission by the author.
The robotic process automation market has helped many clients increase speed, deliver higher accuracy, achieve greater levels of consistency, reduce costs, provide scale, and improve quality. Constellation estimates the market size in 2021 to achieve $2.2B in revenue with a CAGR of 18.8% and growth to $5.07B in 2026.
RPA is a transactional system technology that enables automation of business processes using software robots "bots". RPA tools watch users and then repeat similar tasks in the graphical user interface (GUI). RPA is different than workflow automation tools as those are explicit rules and actions written to automate actions in an unintelligent manner.
RPA tools have reached their limit in terms of capability as transactional automation requires a large overhead of management. Transactional automation is hard to mange. Hence, a new class of enterprise apps known as autonomous applications have emerged to deliver intelligent automation, cognitive capabilities, and artificial intelligence inside organizations in business functions such as finance, supply chain, customer experience, human resources, and planning.
 AI and ML Powers The Future Of Autonomous Enterprises
AI and ML Powers The Future Of Autonomous Enterprises
The reality - traditional transactional applications have run their course. The pressure to reduce margins, technical debt and investment in core systems creates tremendous incentives for the automated enterprise. Customers seek cognitive-based approaches in order to build the true foundation for automation and artificial intelligence–driven precision decisions.
The benefits include less staffing, reduced errors, smarter decisions and security at scale. The quest for an autonomous enterprise starts with a desire to consider what decisions require intelligent automation versus human judgment. These applications can not rely on hard-coded rules to succeed. They must take a cognitive approach, apply AI and ML techniques and become autonomous.
Vendors from multiple fronts intend to deliver on this promise. Legacy enterprise resource planning providers, cloud vendors, business process management solutions, robotic process automation products, process-mining vendors and IT services firms with software solutions attempt to compete with pure-play vendors for both mind share and market dominance in this market, which Constellation Research expects to hit $10.35 billion by 2030. Constellation believes every enterprise will design for self-driving, self-learning, and self-healing sentience.
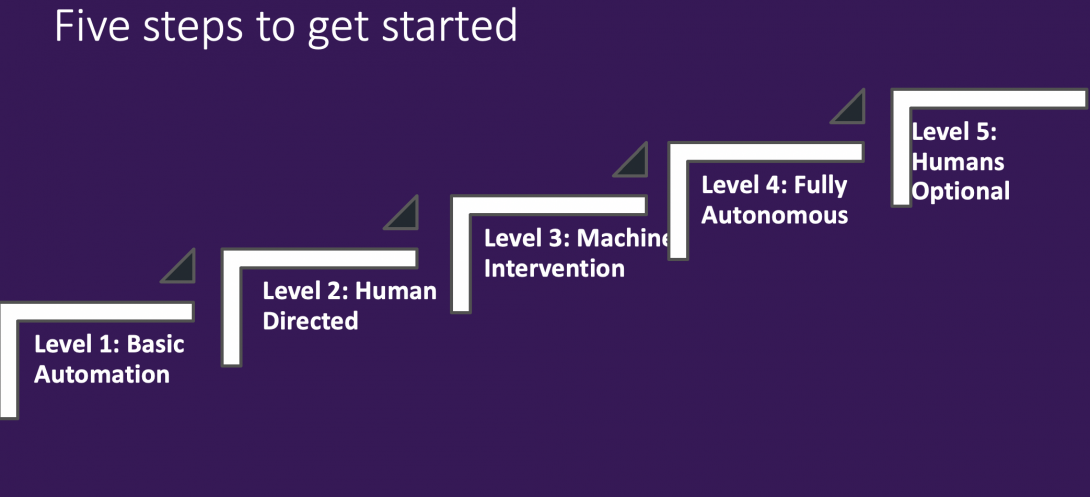
Understand The Five Levels To Full Autonomy And Autonomous Enterprises
Constellation identifies five levels of autonomous enterprises and predicts when these cognitive apps will deliver full autonomy.
Level 1 Autonomous Enterprise: Basic Automation
In this level, the system can provide basic task and workflow automation. In the automotive world, this is akin to basic cruise control.
- When? Today.
- Includes: Basic process automation tools such as BPM, manual instrumentation and control, and intelligent workflow automation
- Who’s in control? Humans are still in control and guide many manual steps.
Level 2 Autonomous Enterprise: Human-Directed
Level 2 enables human-directed automation of business processes. In the automotive world, this is akin to being able to have adaptive cruise control.
- When? Current state of the art
- Includes: Robotic process automation, process-mining tools, journey orchestration tools, ML algorithms, natural language processing.
- Who’s in control? Humans direct major decisions; minor decisions automated over time with some effort in training.
Level 3 Autonomous Enterprise: Machine Intervention
Level 3 delivers automation with occasional machine intervention. In the automotive world, this is when the car brakes on its own with object detection such as when a child is behind a car during backup and the car brakes.
- When? The next big thing in 2020.
- Includes: Cognitive applications, neural networks, GANs models, contextual decisions and next best actions.
- Who’s driving? Humans still on standby but can be hands-off for periods of time
Level 4 Autonomous Enterprise: Fully Autonomous
Level 4 presumes that the machines can deliver full automation but not sentience. Think of autonomous vehicles that can run on their own but humans are still watching.
- When? Sometime in 2023.
- Includes: AI-driven smart services, full automation, self-learning, self-healing and self-securing.
- Who’s driving? Machines are fully automated.
Level 5 Autonomous Enterprise: Humans Optional
Level 5 achieves full sentience and humans may no longer be needed. Think of these as autonomous vehicles with no human intervention and central controls by machines.
- When? 2030.
- Includes: Fully autonomous sentience, empowering precision decisions at scale.
Who’s driving? Humans fully optional.
The Bottom Line: Expect Level 4 Autonomous Enterprises To Emerge In 2023
The pioneering work with early cognitive applications show exponential progress in achieving Level 4 status by 2023. Organizations will have to rethink how they work with their transactional applications, future data-driven digital networks, and distributed compute and storage environments.
The future is autonomous. Machines will deliver services that are continuous, auto-compliant, self-healing, self-learning, and self-aware. The need for greater precision decisions will require connections to data-driven digital networks and for more and more sources of data. This battle for public, private, and shared data will shape who wins in new networked economies that form the future of this autonomous decade.
